4.1 - Intro to React and HTML
What is React?
React is a Javascript library for building user interfaces (UI).
Take a look at this webpage. React allows you, the programmer, to build reusable components, like a sidebar, a clickable button, or a paragraph of text, which helps efficiently create interactive UI's.
Take a look at the Official React Docs.
Why React?
-
Reusablity and Modularity:
- React's component-based architecture, allow developers to create reusable components that manage their own state. Components are modular and can be easily maintained, tested individually, and reused. (Don't Repeat Yourself!)
-
Efficient Updates and Rendering:
- React uses a virtual DOM to optimize updates. Instead of directly manipulating the browser's DOM, React updates a virtual representation of the DOM, which is then used to calculate the most efficient way to update the real DOM.
Deep Dive: DOM and Virtual DOM
The Document Object Model (DOM), is the data representation of a web document. representing it as nodes and objects. This way it can be modified with a scripting language such as JavaScript.
The Virtual DOM is a lightweight copy of the actual DOM. It’s a JavaScript object that React uses to keep track of changes in the UI. When a component’s state changes, React updates the virtual DOM instead of the real DOM.
How does Virtual DOM make React faster?
-
Batching Updates: React batches multiple updates to the virtual DOM, reducing the number of times the real DOM needs to be updated.
-
React compares the new virtual DOM to the previous virtual DOM to identify the minimal set of changes required. This process is called reconciliation.
-
After identifying the changes, React updates only the parts of the real DOM that have changed, rather than re-rendering the entire UI. This selective rendering significantly improves performance, especially for complex UIs.
-
Cross-Platform Development: You can use React in mobile app development, with React Native.
-
Extensive Resources: Check out the beautiful React Official Documentation.
But First ... Basic HTML
Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML):
- Describes the structure of a webpage
- Consists of a series of HTML elements, which label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.
- For further reading check out MDN web docs tutorial-HTML
Deep Dive: Hypertext and Markdown
"Hypertext" refers to links that connect web pages to one another, either within a single website or between websites.
HTML uses "markup" to annotate text, images, and other content for display in a Web browser.
HTML markup includes special "tags" such as <head>, <title>, <body>, <footer>, <article> <p>, <div>, <img>, <ul>, <ol>, <li> and many others.
The syntax of using < and > tells the compiler that the HTML element is a tag and not actual content.
HTML Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
<p>This is another paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Below is a visualization of an HTML page structure:
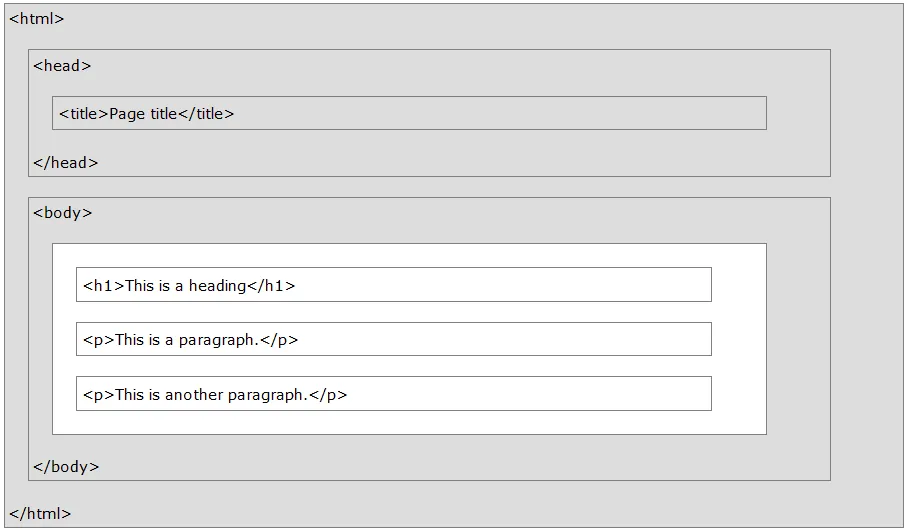
In this case, <title>Page Title</title> would be an HTML element, defined by a start tag:<title>, your content, and an end tag </title>